Difference between revisions of "Ascorbic acid"
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
| − | [ | + | {{Chembox |
| − | '''Ascorbic acid '''is a naturally-occurring organic compound more routinely known as vitamin C. It is found naturally in many fruits and is a well-known antioxidant. It can be easily purchased in tablet or powder form in groceries or pharmacies. In the field of chemistry, it is used as a [[reducing agent]], such as in the precipitation of elemental [[copper]] from a solution of copper(II) ions, as well as a means of introducing the [[ascorbate|ascorbate ion]]. | + | | Name = Ascorbic acid |
| + | | Reference = | ||
| + | | IUPACName = (2R)-2-[(1S)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-3,4-dihydroxy-2H-furan-5-one | ||
| + | | PIN = | ||
| + | | SystematicName = | ||
| + | | OtherNames = Ascoltin<br>Ascorbate<br>Ascorbic acid<br>L-ascorbic acid<br>Vitamin C | ||
| + | <!-- Images --> | ||
| + | | ImageFile = | ||
| + | | ImageSize = | ||
| + | | ImageAlt = | ||
| + | | ImageName = | ||
| + | | ImageFile1 = Ascorbic acid bottle and sample.jpg | ||
| + | | ImageSize1 = 300 | ||
| + | | ImageAlt1 = | ||
| + | | ImageName1 = | ||
| + | | ImageCaption1 = L(+) ascorbic acid sample and original bottle | ||
| + | | ImageFile2 = L-Ascorbic acid structure.png | ||
| + | | ImageSize2 = 280 | ||
| + | | ImageAlt2 = | ||
| + | | ImageName2 = | ||
| + | | ImageCaption2 = The structure of ascorbic acid. | ||
| + | | ImageFile3 = | ||
| + | | ImageSize3 = | ||
| + | | ImageAlt3 = | ||
| + | | ImageName3 = | ||
| + | | ImageFileL1 = | ||
| + | | ImageSizeL1 = | ||
| + | | ImageAltL1 = | ||
| + | | ImageNameL1 = | ||
| + | | ImageFileR1 = | ||
| + | | ImageSizeR1 = | ||
| + | | ImageAltR1 = | ||
| + | | ImageNameR1 = | ||
| + | | ImageFileL2 = | ||
| + | | ImageSizeL2 = | ||
| + | | ImageAltL2 = | ||
| + | | ImageNameL2 = | ||
| + | | ImageFileR2 = | ||
| + | | ImageSizeR2 = | ||
| + | | ImageAltR2 = | ||
| + | | ImageNameR2 = | ||
| + | <!-- Sections --> | ||
| + | | Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | ||
| + | | 3DMet = | ||
| + | | Abbreviations = | ||
| + | | SMILES = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section2 = {{Chembox Properties | ||
| + | | AtmosphericOHRateConstant = | ||
| + | | Appearance = White solid | ||
| + | | BoilingPt = | ||
| + | | BoilingPtC = 192 | ||
| + | | BoilingPt_ref = | ||
| + | | BoilingPt_notes = (decomposes) | ||
| + | | Density = 1.694 g/cm<sup>3</sup> | ||
| + | | Formula = C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>8</sub>O<sub>6</sub> | ||
| + | | HenryConstant = | ||
| + | | LogP = | ||
| + | | MolarMass = 176.12 g/mol | ||
| + | | MeltingPt = | ||
| + | | MeltingPtC = 190 | ||
| + | | MeltingPt_ref = | ||
| + | | MeltingPt_notes = | ||
| + | | Odor = Odorless | ||
| + | | pKa = | ||
| + | | pKb = | ||
| + | | Solubility = 30 g/100 ml (at 20 °C)<br>40 g/100 ml (at 40 °C) | ||
| + | | SolubleOther = Slightly soluble in [[alcohol]]s<br>Insoluble in [[benzene]], [[chloroform]], [[dichloromethane]], [[diethyl ether]], [[petroleum ether]], [[toluene]], [[xylene]], oils, lipids | ||
| + | | Solubility1 = 3.3 g/100 ml | ||
| + | | Solvent1 = ethanol | ||
| + | | Solubility2 = 2 g/100 ml | ||
| + | | Solvent2 = ethanol 95 % | ||
| + | | Solubility3 = 1 g/100 ml | ||
| + | | Solvent3 = glycerol | ||
| + | | Solubility4 = 5 g/100 ml | ||
| + | | Solvent4 = propylene glycol | ||
| + | | VaporPressure = 9.28·10<sup>-11</sup> mmHg (25 °C) | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section3 = {{Chembox Structure | ||
| + | | Coordination = | ||
| + | | CrystalStruct = | ||
| + | | MolShape = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section4 = {{Chembox Thermochemistry | ||
| + | | DeltaGf = | ||
| + | | DeltaHc = | ||
| + | | DeltaHf = | ||
| + | | Entropy = | ||
| + | | HeatCapacity = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section5 = {{Chembox Explosive | ||
| + | | ShockSens = | ||
| + | | FrictionSens = | ||
| + | | DetonationV = | ||
| + | | REFactor = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section6 = {{Chembox Hazards | ||
| + | | AutoignitionPt = 380 °C (716 °F; 653 K) | ||
| + | | ExploLimits = | ||
| + | | ExternalMSDS = [https://www.docdroid.net/9wODaQI/l-ascorbic-acid-sa.pdf.html Sigma-Aldrich] | ||
| + | | FlashPt = | ||
| + | | LD50 = 11,900 mg/kg (rat, oral) | ||
| + | | LC50 = | ||
| + | | MainHazards = | ||
| + | | NFPA-F = | ||
| + | | NFPA-H = | ||
| + | | NFPA-R = | ||
| + | | NFPA-S = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section7 = {{Chembox Related | ||
| + | | OtherAnions = | ||
| + | | OtherCations = | ||
| + | | OtherFunction = | ||
| + | | OtherFunction_label = | ||
| + | | OtherCompounds = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | '''Ascorbic acid '''is a naturally-occurring organic compound more routinely known as '''vitamin C'''. It is found naturally in many fruits and is a well-known antioxidant. It can be easily purchased in tablet or powder form in groceries or pharmacies. In the field of chemistry, it is used as a [[reducer|reducing agent]], such as in the precipitation of elemental [[copper]] from a solution of copper(II) ions, as well as a means of introducing the [[ascorbate|ascorbate ion]]. | ||
==Properties== | ==Properties== | ||
| Line 11: | Line 128: | ||
==Availability== | ==Availability== | ||
| − | Ascorbic acid is sold in pharmacies. | + | Ascorbic acid is sold in pharmacies an most food stores. It is also sometimes sold in the winemaking sections of stores. |
| − | ==Preparation== | + | ==Preparation and isolation== |
| − | Ascorbic acid | + | Ascorbic acid is much cheaper to be extracted from fruits than synthesized from precursors. However you will need large amounts of fruits to get useful amounts of ascorbic acid. Extraction from vitamin C supplements is easier, especially since vitamin C is very cheap. |
==Projects== | ==Projects== | ||
*Reduce various metals compounds to their respective metals | *Reduce various metals compounds to their respective metals | ||
| + | *Destroy Cr(VI) ions | ||
| + | *Vitamin C (food-grade only!) | ||
==Handling== | ==Handling== | ||
| Line 24: | Line 143: | ||
===Storage=== | ===Storage=== | ||
| − | + | Ascorbic acid should be kept in closed bottles. | |
===Disposal=== | ===Disposal=== | ||
| − | Ascorbic acid can be safely poured down the drain, dumped in soil or burned. | + | Ascorbic acid can be safely poured down the drain, dumped in trash, soil or just burned, as it is practically non-toxic. |
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
===Relevant Sciencemadness threads=== | ===Relevant Sciencemadness threads=== | ||
| + | *[http://www.sciencemadness.org/talk/viewthread.php?tid=64349 Vitamin C] | ||
| + | *[http://www.sciencemadness.org/talk/viewthread.php?tid=64010 Ascorbic acid complexes] | ||
| + | *[http://www.sciencemadness.org/talk/viewthread.php?tid=3871 Extracting Vitamin C From The Juice Of Orange Or Lemon] | ||
[[Category:Chemical compounds]] | [[Category:Chemical compounds]] | ||
| Line 39: | Line 161: | ||
[[Category:Furones]] | [[Category:Furones]] | ||
[[Category:Reducing agents]] | [[Category:Reducing agents]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Readily available chemicals]] | ||
[[Category:Materials available as food grade]] | [[Category:Materials available as food grade]] | ||
[[Category:Edible chemicals]] | [[Category:Edible chemicals]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Essential reagents]] | ||
Revision as of 09:23, 16 June 2019
 |
This article is a stub. Please help Sciencemadness Wiki by expanding it, adding pictures, and improving existing text.
|
 L(+) ascorbic acid sample and original bottle
| |
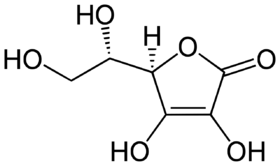 The structure of ascorbic acid.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2R)-2-[(1S)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-3,4-dihydroxy-2H-furan-5-one
| |
| Other names
Ascoltin
Ascorbate Ascorbic acid L-ascorbic acid Vitamin C | |
| Properties | |
| C6H8O6 | |
| Molar mass | 176.12 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.694 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 190 °C (374 °F; 463 K) |
| Boiling point | 192 °C (378 °F; 465 K) (decomposes) |
| 30 g/100 ml (at 20 °C) 40 g/100 ml (at 40 °C) | |
| Solubility | Slightly soluble in alcohols Insoluble in benzene, chloroform, dichloromethane, diethyl ether, petroleum ether, toluene, xylene, oils, lipids |
| Solubility in ethanol | 3.3 g/100 ml |
| Solubility in ethanol 95 % | 2 g/100 ml |
| Solubility in glycerol | 1 g/100 ml |
| Solubility in propylene glycol | 5 g/100 ml |
| Vapor pressure | 9.28·10-11 mmHg (25 °C) |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (Median dose)
|
11,900 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Ascorbic acid is a naturally-occurring organic compound more routinely known as vitamin C. It is found naturally in many fruits and is a well-known antioxidant. It can be easily purchased in tablet or powder form in groceries or pharmacies. In the field of chemistry, it is used as a reducing agent, such as in the precipitation of elemental copper from a solution of copper(II) ions, as well as a means of introducing the ascorbate ion.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Ascorbic acid can be used to reduce silver nitrate to metallic silver.
Physical
Ascorbic acid is a white to light yellow solid, soluble in water, with a sour taste. It is soluble in water, less so in alcohols, glycerol, propylene glycol, and insoluble in benzene, chloroform, diethyl ether, petroleum ether, as well as fats and oils.
Availability
Ascorbic acid is sold in pharmacies an most food stores. It is also sometimes sold in the winemaking sections of stores.
Preparation and isolation
Ascorbic acid is much cheaper to be extracted from fruits than synthesized from precursors. However you will need large amounts of fruits to get useful amounts of ascorbic acid. Extraction from vitamin C supplements is easier, especially since vitamin C is very cheap.
Projects
- Reduce various metals compounds to their respective metals
- Destroy Cr(VI) ions
- Vitamin C (food-grade only!)
Handling
Safety
Ascorbic acid is vital to the organism. Lack of ascorbic acid leads to scurvy.
Storage
Ascorbic acid should be kept in closed bottles.
Disposal
Ascorbic acid can be safely poured down the drain, dumped in trash, soil or just burned, as it is practically non-toxic.