Haematoxylin
 |
This article is a stub. Please help Sciencemadness Wiki by expanding it, adding pictures, and improving existing text.
|
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
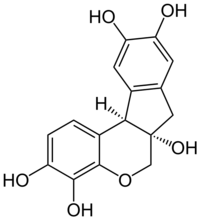
| IUPAC name
7,11b-Dihydroindeno[2,1-c]chromene-3,4,6a,9,10(6H)-pentol
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H14O6 | |
| Molar mass | 302.28 g/mol |
| Appearance | White to yellowish solid |
| Melting point | 120 °C (248 °F; 393 K) (decomposes) |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
| Slightly soluble | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Haematoxylin also called hematoxylin, natural black 1 or C.I. 75290 is a compound extracted from the heartwood of the logwood tree. Hematoxylin is a basic / positive compound that binds to and forms salts with acidic, or basophilic, compounds containing negative charges (such as DNA and RNA which are acidic/negative because the nucleic acid building blocks that come off the phosphate backbone are negatively charged) and stains them dark blue or violet. Haematoxylin and eosin together make up haematoxylin and eosin stain, one of the most commonly used stains in histology. This type of stain is a permanent stain as opposed to temporary stains (e.g. iodine solution in KI).
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Physical
Availability
Delete this section if not applicable
Preparation
Delete this section if not applicable