Difference between revisions of "Sodium perchlorate"
Diachrynic (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
| pKa = | | pKa = | ||
| pKb = | | pKb = | ||
| − | | Solubility = 209.6 g/100 ml (25 °C, anhydrous)<br>209 g/100 | + | | Solubility = 209.6 g/100 ml (25 °C, anhydrous)<br>209 g/100 ml (15 °C, monohydrate) |
| − | | SolubleOther = Insoluble in [[benzene]], [[chloroform]], [[toluene]] | + | | SolubleOther = Soluble in [[acetone]], [[ethyl acetate]] and short alcohols<br>Insoluble in [[benzene]], [[chloroform]], [[toluene]], [[diethyl ether]]<ref name="gmelinna" /> |
| − | | | + | | Solubility1 = 52 g/100 g<ref name="gmelinna">''Gmelins Handbuch der anorganischen Chemie, Natrium'', Verlag Chemie GmbH, Berlin, 8th edition '''1928''', p. 413</ref> |
| + | | Solvent1 = acetone | ||
| + | | Solubility2 = 51 g/100 g<ref name="gmelinna" /> | ||
| + | | Solvent2 = methanol | ||
| + | | Solubility3 = 14.7 g/100 g<ref name="gmelinna" /> | ||
| + | | Solvent3 = ethanol | ||
| + | | Solubility4 = 4.9 g/100 g<ref name="gmelinna" /> | ||
| + | | Solvent4 = propanol | ||
| + | | Solubility5 = 1.9 g/100 g<ref name="gmelinna" /> | ||
| + | | Solvent5 = butanol | ||
| VaporPressure = ~0 mmHg | | VaporPressure = ~0 mmHg | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 90: | Line 99: | ||
| Section6 = {{Chembox Hazards | | Section6 = {{Chembox Hazards | ||
| AutoignitionPt = Non-flammable | | AutoignitionPt = Non-flammable | ||
| − | | ExploLimits = | + | | ExploLimits = Non-flammable |
| ExternalMSDS = [http://www.sciencelab.com/msds.php?msdsId=9925018 ScienceLab] (anhydrous)<br>[http://www.sciencelab.com/msds.php?msdsId=9927599 ScienceLab] (monohydrate) | | ExternalMSDS = [http://www.sciencelab.com/msds.php?msdsId=9925018 ScienceLab] (anhydrous)<br>[http://www.sciencelab.com/msds.php?msdsId=9927599 ScienceLab] (monohydrate) | ||
| FlashPt = Non-flammable | | FlashPt = Non-flammable | ||
| Line 117: | Line 126: | ||
It will react with a strong mineral acid, such as [[sulfuric acid]], to form [[perchloric acid]]. This can be isolated by vacuum distillation. | It will react with a strong mineral acid, such as [[sulfuric acid]], to form [[perchloric acid]]. This can be isolated by vacuum distillation. | ||
| − | :NaClO<sub>4</sub>(aq) + H<sub>2</sub>SO<sub>4</sub>(aq) ↔ NaHSO<sub>4</sub> (aq) + HClO<sub>4</sub>(aq) | + | : NaClO<sub>4</sub>(aq) + H<sub>2</sub>SO<sub>4</sub>(aq) ↔ NaHSO<sub>4</sub> (aq) + HClO<sub>4</sub>(aq) |
===Physical=== | ===Physical=== | ||
| − | Sodium perchlorate is a white crystalline salt. It is hygroscopic, forming a monohydrate. It is highly soluble in water, 209 g/100 ml at 25 °C. It is also soluble in low chain alcohols. | + | Sodium perchlorate is a white crystalline salt. It is hygroscopic, forming a monohydrate. It is highly soluble in water, 209 g/100 ml at 25 °C. It is also soluble in low chain alcohols. For other solubilities refer to the info box. It is soluble in iso-butanol at 0.79 g/100 g and in [[ethyl acetate]] at 9.6 g/100 g.<ref name="gmelinna" /> |
==Availability== | ==Availability== | ||
| Line 128: | Line 137: | ||
Sodium perchlorate is produced by anodic oxidation of [[sodium chlorate]] (which in turn is made from the electrolysis of a solution of [[sodium chloride]]) at an inert electrode, such as [[platinum]].<ref>http://www.utahpyro.org/compositions/HowToMakeSodiumPerchlorate.pdf</ref> | Sodium perchlorate is produced by anodic oxidation of [[sodium chlorate]] (which in turn is made from the electrolysis of a solution of [[sodium chloride]]) at an inert electrode, such as [[platinum]].<ref>http://www.utahpyro.org/compositions/HowToMakeSodiumPerchlorate.pdf</ref> | ||
| − | :ClO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup> (aq) + H<sub>2</sub>O (l) → ClO<sub>4</sub><sup>-</sup> (aq) + H<sub>2</sub> (g) | + | : ClO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup> (aq) + H<sub>2</sub>O (l) → ClO<sub>4</sub><sup>-</sup> (aq) + H<sub>2</sub> (g) |
| − | However when using platinum as an anode, its wear rate will increase as the chlorate concentration starts to decrease, and below | + | However when using platinum as an anode, its wear rate will increase as the chlorate concentration starts to decrease, and below 50 g/l it may be excessive; high temperatures also increase its wear rate. Wear rates from manufacturers have been reported as 3 to 6 grams of Pt per ton of sodium perchlorate.<ref>http://www.oocities.org/capecanaveral/campus/5361/chlorate/naperchl.html</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | Sodium perchlorate can also be prepared by thermal decomposition of sodium chlorate, yielding sodium chloride as side product. Since the sodium perchlorate can also decompose and the sodium chlorate can give off oxygen without making perchlorate, this can be a lossy way to produce this compound. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :4 NaClO<sub>3</sub> → NaCl + 3 NaClO<sub>4</sub> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The reaction is considerably faster than a perchlorate cell however. The main drawbacks are the difficulty in holding the temperature (since sodium perchlorate also decomposes) and the danger of the molten chlorate. It is doubtful if this method scales well. The resulting reaction mixture can be separated by dissolution of the perchlorate in [[acetone]], since both sodium chlorate and sodium chloride are rather poorly soluble in it.<ref>Liptakov's video on producing sodium perchlorate from sodium chlorate by thermal decomposition: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1Ylt2ZKJlME</ref><ref>https://patents.google.com/patent/US3151935A/en</ref> | ||
==Projects== | ==Projects== | ||
*Make [[potassium perchlorate]] | *Make [[potassium perchlorate]] | ||
| − | *Make perchloric acid | + | *Make [[perchloric acid]] |
| − | *Flash powder | + | *[[Flash powder]] |
*Chemical oxygen generator | *Chemical oxygen generator | ||
| Line 151: | Line 166: | ||
Sodium perchlorate can be destroyed with metallic [[iron]] under UV light, in the absence of air.<ref>[https://books.google.ro/books?id=gjfSBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA106&lpg=PA106&dq=perchlorate+neutralization&source=bl&ots=ztEPz18eE-&sig=oHHZzByFHPVjYIVxbvzGl4SC_xQ&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwi5gpTJm_XJAhVBURoKHb3LB4o4ChDoAQguMAc#v=onepage&q=perchlorate%20neutralization&f=false Perchlorate in the Environment (2000), Edward Todd Urbansky, pag. 106]</ref> | Sodium perchlorate can be destroyed with metallic [[iron]] under UV light, in the absence of air.<ref>[https://books.google.ro/books?id=gjfSBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA106&lpg=PA106&dq=perchlorate+neutralization&source=bl&ots=ztEPz18eE-&sig=oHHZzByFHPVjYIVxbvzGl4SC_xQ&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwi5gpTJm_XJAhVBURoKHb3LB4o4ChDoAQguMAc#v=onepage&q=perchlorate%20neutralization&f=false Perchlorate in the Environment (2000), Edward Todd Urbansky, pag. 106]</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Gallery== | ||
| + | <gallery widths="200" position="center" columns="4" orientation="none"> | ||
| + | Sodium_perchlorate_in_acetone.jpg|Sodium perchlorate crystals forming in acetone solution. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 157: | Line 177: | ||
*[https://www.sciencemadness.org/whisper/viewthread.php?tid=17629 pH control of a Sodium Perchlorate cell] | *[https://www.sciencemadness.org/whisper/viewthread.php?tid=17629 pH control of a Sodium Perchlorate cell] | ||
*[https://www.sciencemadness.org/whisper/viewthread.php?tid=23141 Seeking help regarding unsuccessful sodium perchlorate cell] | *[https://www.sciencemadness.org/whisper/viewthread.php?tid=23141 Seeking help regarding unsuccessful sodium perchlorate cell] | ||
| + | *[https://www.sciencemadness.org/whisper/viewthread.php?tid=158481 Separating Sodium Perchlorate from Buffer Solution] | ||
[[Category:Chemical compounds]] | [[Category:Chemical compounds]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:06, 14 August 2023
 Sodium perchlorate sample
| |
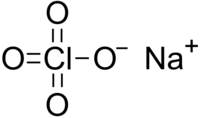
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Sodium perchlorate
| |
| Other names
Sodium chlorate(VII)
Sodium hyperchlorate | |
| Identifiers | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| |
| Properties | |
| NaClO4 | |
| Molar mass | 122.44 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 2.4994 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 2.02 g/cm3 (monohydrate) |
| Melting point | 468 °C (874 °F; 741 K) (decomposes, anhydrous) 130 °C (266 °F; 403.15 K) (monohydrate) |
| Boiling point | 482 °C (900 °F; 755 K) (monohydrate, decomposes) |
| 209.6 g/100 ml (25 °C, anhydrous) 209 g/100 ml (15 °C, monohydrate) | |
| Solubility | Soluble in acetone, ethyl acetate and short alcohols Insoluble in benzene, chloroform, toluene, diethyl ether[1] |
| Solubility in acetone | 52 g/100 g[1] |
| Solubility in methanol | 51 g/100 g[1] |
| Solubility in ethanol | 14.7 g/100 g[1] |
| Solubility in propanol | 4.9 g/100 g[1] |
| Solubility in butanol | 1.9 g/100 g[1] |
| Vapor pressure | ~0 mmHg |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | ScienceLab (anhydrous) ScienceLab (monohydrate) |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds
|
Sodium hypochlorite Sodium chlorite Sodium chlorate |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Sodium perchlorate is an inorganic salt of sodium, with the chemical formula NaClO4.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Sodium perchlorate is a powerful oxidizer, though it's not as useful in pyrotechnics as the potassium salt due to its hygroscopicity.
It will react with a strong mineral acid, such as sulfuric acid, to form perchloric acid. This can be isolated by vacuum distillation.
- NaClO4(aq) + H2SO4(aq) ↔ NaHSO4 (aq) + HClO4(aq)
Physical
Sodium perchlorate is a white crystalline salt. It is hygroscopic, forming a monohydrate. It is highly soluble in water, 209 g/100 ml at 25 °C. It is also soluble in low chain alcohols. For other solubilities refer to the info box. It is soluble in iso-butanol at 0.79 g/100 g and in ethyl acetate at 9.6 g/100 g.[1]
Availability
Sodium perchlorate used to be available globally, but recent regulations have restricted its possession in Europe. Perchlorates can still be purchased from some online vendors, but in limited quantities. Purchases using some form of identification have a good chance of being tracked by a government agency. In the US, perchlorates are still widely available through pyrotechnic companies as well as lab suppliers.
Preparation
Sodium perchlorate is produced by anodic oxidation of sodium chlorate (which in turn is made from the electrolysis of a solution of sodium chloride) at an inert electrode, such as platinum.[2]
- ClO3- (aq) + H2O (l) → ClO4- (aq) + H2 (g)
However when using platinum as an anode, its wear rate will increase as the chlorate concentration starts to decrease, and below 50 g/l it may be excessive; high temperatures also increase its wear rate. Wear rates from manufacturers have been reported as 3 to 6 grams of Pt per ton of sodium perchlorate.[3]
Sodium perchlorate can also be prepared by thermal decomposition of sodium chlorate, yielding sodium chloride as side product. Since the sodium perchlorate can also decompose and the sodium chlorate can give off oxygen without making perchlorate, this can be a lossy way to produce this compound.
- 4 NaClO3 → NaCl + 3 NaClO4
The reaction is considerably faster than a perchlorate cell however. The main drawbacks are the difficulty in holding the temperature (since sodium perchlorate also decomposes) and the danger of the molten chlorate. It is doubtful if this method scales well. The resulting reaction mixture can be separated by dissolution of the perchlorate in acetone, since both sodium chlorate and sodium chloride are rather poorly soluble in it.[4][5]
Projects
- Make potassium perchlorate
- Make perchloric acid
- Flash powder
- Chemical oxygen generator
Handling
Safety
Sodium perchlorate is a powerful oxidizer. It should be kept away from organic substances and strong reducing agents. Unlike chlorates, perchlorate mixtures with sulfur are relatively stable.
It is moderately toxic, as in large amounts it interferes with iodine uptake into the thyroid gland.
Storage
NaClO4 should be stored in tightly sealed bottles as it is slightly hygroscopic. It should be kept away from any strong acidic vapors to prevent the formation of anhydrous perchloric acid, a fire and explosion hazard. It must also be kept away from any flammable materials.
Disposal
Sodium perchlorate should not be poured down the drain or dumped into environment. It must be neutralized with a reducing agent to NaCl first.
Sodium perchlorate can be destroyed with metallic iron under UV light, in the absence of air.[6]
Gallery
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Gmelins Handbuch der anorganischen Chemie, Natrium, Verlag Chemie GmbH, Berlin, 8th edition 1928, p. 413
- ↑ http://www.utahpyro.org/compositions/HowToMakeSodiumPerchlorate.pdf
- ↑ http://www.oocities.org/capecanaveral/campus/5361/chlorate/naperchl.html
- ↑ Liptakov's video on producing sodium perchlorate from sodium chlorate by thermal decomposition: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1Ylt2ZKJlME
- ↑ https://patents.google.com/patent/US3151935A/en
- ↑ Perchlorate in the Environment (2000), Edward Todd Urbansky, pag. 106
Relevant Sciencemadness threads
- Chemical pages without CAS Registry Number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Chemical compounds
- Inorganic compounds
- Oxidizing agents
- Sodium compounds
- Perchlorates
- Neutral salts
