Difference between revisions of "Desiccant"
From Sciencemadness Wiki
(→Comparison) |
(→Comparison) |
||
| Line 132: | Line 132: | ||
| style="text-align: center;"| | | style="text-align: center;"| | ||
| style="text-align: center;"| | | style="text-align: center;"| | ||
| − | | style="text-align: center;"| | + | | style="text-align: center;"| High |
| style="text-align: center;"| No | | style="text-align: center;"| No | ||
| − | | Reaction is very slow, rarely used | + | | Reaction is very slow, rarely used; Mostly used for removing traces of water |
|- | |- | ||
| [[Magnesium sulfate]] | | [[Magnesium sulfate]] | ||
| Line 155: | Line 155: | ||
| style="text-align: center;"| High | | style="text-align: center;"| High | ||
| style="text-align: center;"| Yes | | style="text-align: center;"| Yes | ||
| − | | Unsuitable for drying ketones | + | | Drying takes hours to days; Unsuitable for drying ketones |
|- | |- | ||
| [[Potassium carbonate]] | | [[Potassium carbonate]] | ||
| Line 229: | Line 229: | ||
| [[Zinc chloride]] | | [[Zinc chloride]] | ||
| style="text-align: center;"| Acidic | | style="text-align: center;"| Acidic | ||
| − | | style="text-align: center;"| | + | | style="text-align: center;"| Low |
| − | | style="text-align: center;"| | + | | style="text-align: center;"| Low |
| style="text-align: center;"| Yes | | style="text-align: center;"| Yes | ||
| Regenerating must be done in a stream of hydrogen chloride | | Regenerating must be done in a stream of hydrogen chloride | ||
Revision as of 14:23, 9 July 2016
A desiccant is a chemical which is hygroscopic enough to absorb water from hydrated compounds in the same sealed environment.
Common desiccants
- Calcium
- Calcium chloride
- Calcium oxide
- Concentrated sulfuric acid
- Copper sulfate (anhydrous)
- Magnesium sulfate
- Phosphorus pentoxide
- Silica gel
- Sodium and other alkali metals
- Sodium hydroxide
- Sodium oxide
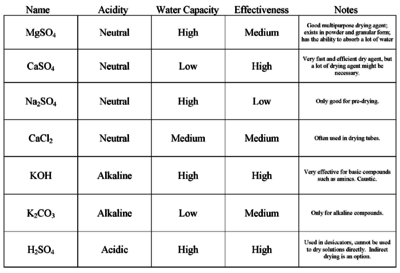
Comparison
| Substance1 | pH | Water capacity | Effectiveness | Reversible | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetonitrile | High | High | Yes | Rarely used | |
| Activated alumina | Basic or acidic | Medium | High | Yes | Can also be used to adsorb fluorides |
| Activated charcoal | Medium | Medium | Yes | Will also adsorb other gasses | |
| Aerogel | High | High | Yes | Expensive | |
| Aluminium nitrate | Slightly acidic | Medium | Medium | No | |
| Bentonite clay | |||||
| Calcium | Alkaline | High | Very high | No | Reaction with water releases large amounts of hydrogen |
| Calcium chloride | Neutral | High | Medium | Yes | Deliquescent; often used in drying tubes |
| Calcium hydride | Alkaline | High | Very high | No | |
| Calcium nitrate | Neutral | Medium | Medium | Yes | |
| Calcium oxide | Alkaline | High | High | No | Calcium oxide will only remove water from ethanol until 5000 ppm.[1] |
| Calcium sulfate | Neutral | Low | High | Yes | Very fast and efficient drying agent, but a lot of drying agent might be necessary |
| Cement (Portland) | Alkaline | Medium | Medium | No | Used in desiccators, cannot be used directly |
| Cobalt(II) chloride | Yes | Mostly used as water indicator | |||
| Copper(II) sulfate | Neutral | Low | Medium | Yes | Mostly used as water indicator |
| Magnesium | High | No | Reaction is very slow, rarely used; Mostly used for removing traces of water | ||
| Magnesium sulfate | Neutral | High | Medium | Yes | Good multipurpose drying agent; exists in powder and granular form; has the ability to absorb a lot of water |
| Magnesium chloride | Neutral | High | Medium | Yes | Deliquescent |
| Molecular sieves | Weakly basic | High | High | Yes | Drying takes hours to days; Unsuitable for drying ketones |
| Potassium carbonate | Acidic | Medium | High | No | Good for thoroughly drying predried compounds |
| Potassium carbonate | Alkaline | Low | Medium | Yes | Only for alkaline compounds |
| Potassium hydroxide | Alkaline | High | High | Yes | |
| Silica gel | Weakly acidic | High | Medium | Yes | |
| Sodium | Alkaline | High | Very High | No | More often used to remove traces of water from aprotic solvents |
| Sodium hydroxide | Alkaline | High | High | Yes | Very effective for basic compounds, such as amines; caustic |
| Sodium oxide | Alkaline | High | Very High | No | More effective when used to dry compounds predried with another desiccant |
| Sodium sulfate | Neutral | High | Low | Yes | Used to dry solvents; Requires lots of it; only good for predrying; |
| Sulfur trioxide | Acidic | High | Very high | No | Tends to form a mist of sulfuric acid in contact with moist air |
| Sulfuric acid (concentrated) | Acidic | High | High | Yes, difficult | Used in desiccators, cannot be used to dry solutions directly |
| Zinc chloride | Acidic | Low | Low | Yes | Regenerating must be done in a stream of hydrogen chloride |
1All compounds are considered anhydrous.
Gallery
- ↑ Ford, S. G.; Marvel, C. S., Organic Syntheses; Wiley: New York, 1943; Collect. Vol. 11, p 373.