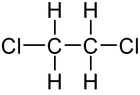
1,2-Dichloroethane
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,2-Dichloroethane
| |||
| Other names
DCA
DCE Dutch liquid Dutch oil Ethane dichloride Ethylene dichloride Freon 150 | |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H4Cl2 | |||
| Molar mass | 98.954 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Odor | Chloroform-like | ||
| Density | 1.253 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −35 °C (−31 °F; 238 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 84 °C (183 °F; 357 K) | ||
| 0.87 g/100 ml (20 °C) | |||
| Solubility | Miscible with alcohols, aromatics, ethers, , halocarbons, ketones | ||
| Vapor pressure | 78.9 mmHg at 25 °C | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich | ||
| Flash point | 13 °C (55 °F; 286 K) | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
| LD50 (Median dose)
|
670 mg/kg (rat, oral) | ||
| LC50 (Median concentration)
|
3,000 ppm (guinea pig, 7 hr) 1,000 ppm (rat, 7 hr) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Related compounds
|
Dichloromethane | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
1,2-dichloroethane, or ethylene dichloride, is a common solvent and reagent, going by the abbreviations EDC and 1,2-DCA. It is also used to make vinyl chloride, the major precursor to polyvinyl chloride, commonly known as PVC.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Ethylene dichloride is a slightly reactive polar solvent. It is sometimes used as a precursor to ethylenediamine.
Physical
Ethylene dichloride is colorless and has a high index of refraction, giving it a shiny appearance, similar to chloroform, which it also shares a similar smells. It is a versatile solvent, though it does form azeotropes with water and many other solvents.
Availability
1,2-Dichloroethane is mostly bought from chemical suppliers rather than ordinary retail stores due to its inherent dangers. In some countries, however, it is sold in hobby stores with no questions asked as a solvent for fusing plastic parts to each other, most often mixed with various hydrocarbons. You can purify the compound from the mixture via fractional distillation.
Preparation
The main industrial route involves the reaction of ethylene and chlorine, in the presence of anh. iron(III) chloride catalyst:
- H2C=CH2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → Cl-C2H4-Cl (l)
Carbon tetrachloride is used as reaction solvent.
A more accessible route involves bubbling oxygen through a solution containing ethylene and hydrochloric acid/hydrogen chloride (oxychlorination), in the presence of copper(II) chloride catalyst, process which yields dichloroethane, and water being produced as side product.
- H2C=CH2 + 2 HCl + ½ O2 → Cl-C2H4-Cl + H2O
Projects
- Ethylenediamine synthesis
- Make PVC
- Extraction solvent
Handling
Safety
Ethylene dichloride is toxic (by inhalation), flammable, and a carcinogen. All these hazards are amplified by the chemical's volatile nature. This chemical is also unstable when in the presence of aluminium, zinc and iron[1].
Storage
Dichloroethane should be stored in closed amber glass bottles, in dark well ventilated places.
Disposal
Dichloroethane can be neutralized by reducing it with a metal powder, like iron, over the course of several days or with Fenton's reagent. Both processes release heat, which may volatilize some dichloroethane. This should be performed in a fume hood or outside.