VeritasC&E
Hazard to Others
Posts: 176
Registered: 29-1-2018
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
Specific Retention Capacity and Efficiency of Common Activated Carbon Types?
After doing some research I've come to the assumption that activated carbons are good at retaining (A) Non-Polar Molecules (through Van Der Waals
Adsorption) and (B) Small Molecules (through London Dispersion Force); whatever these forces may be.
Now I'm wondering if there exists a table with retention capacity and efficiency data vs specific molecules for (standardized) common activated carbon
types? Or if maybe that's something useful we could compile together from different sources?
It would be really nice to co-compile a comprehensive guide on AC, including such things as preferred solvent type(s), preferred solvent
concentration, ideal medium temperature, etc.
[Edited on 1-8-2021 by VeritasC&E]
|
|
|
Plunkett
Hazard to Self
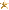 
Posts: 96
Registered: 16-4-2017
Location: The Richest Hill on Earth
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
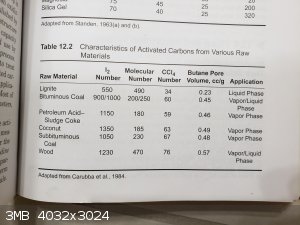
This table from Air Pollution Control: A Design Approach by C. Cooper has data for the sorption of I2 and CCl4 by
activated carbon from different sources. The I2 number is g of I2/100 g carbon after the carbon is saturated in a flowing
stream of I2, and the CCl4 number is g CCl4/100 g carbon.
[Edited on 8/1/2021 by Plunkett]
|
|
|
VeritasC&E
Hazard to Others
Posts: 176
Registered: 29-1-2018
Member Is Offline
Mood: No Mood
|
|
Quote: Originally posted by Plunkett  | This table from Air Pollution Control: A Design Approach by C. Cooper has data for the sorption of I2 and CCl4 by
activated carbon from different sources. The I2 number is g of I2/100 g carbon after the carbon is saturated in a flowing
stream of I2, and the CCl4 number is g CCl4/100 g carbon.
[Edited on 8/1/2021 by Plunkett] |
Hi Plunkett! Thank you for your contribution!
Now we have data for typical CCl4 and I2 values for several types of AC (I2 being probably the most standard indicator parameter, along with surface
area, for a given AC's general adsorption capacity).
The idea would be that together we make such a table with retention capacity and efficiency for each of the most common molecules we come across. A
few years back I came across a paper that listed typical values, even including retention values for heavy metal species (from what I recall this was
among the worst performance of AC, but different treatments would still yield some degree of heavy metal retention by AC). I can't find that paper
anymore but it surely would provide us with retention capacity values for few molecules.
|
|
|