Lead picrate
From Sciencemadness Wiki
 |
This article is a stub. Please help Sciencemadness Wiki by expanding it, adding pictures, and improving existing text.
|

| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
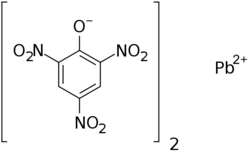
| IUPAC name
lead(2+);2,4,6-trinitrophenolate
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
2,4-Dinitro-6-(oxo{[(2,4,6-trinitrophenoxy)-λ2-plumbanyl]oxy}ammonio)phenolate | |
| Identifiers | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H4N6O14Pb | |
| Molar mass | 663.4g/mol |
| Appearance | Dense, orange powder |
| Melting point | Detonates |
| Boiling point | Detonates |
| barely soluble in water at 20°C | |
| Hazards | |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds
|
Picric acid, Lead styphnate, Lead(II) azide |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Lead picrate, or more properly,basic lead picrate, is an energetic, toxic, and explosive lead salt.
Properties
Physical
Lead picrate is an orange, very dense non-hygroscopic lead compound. Its melting and boiling point are both unknown, as it tends to deflagrate or detonate before it reaches such a temperature.
