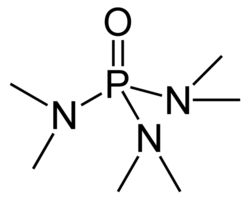
Hexamethylphosphoramide
 HMPA chemical structure
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Hexamethylphosphoramide
| |
| Preferred IUPAC name
Hexamethylphosphoric triamide | |
| Other names
Hexametapol
HMPA N,N,N',N',N' ',N' '-hexamethylphosphoric triamide | |
| Properties | |
| C6H18N3OP [(CH3)2N]3PO | |
| Molar mass | 179.20 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Aromatic, "spicy" odor |
| Density | 1.03 g/cm3 (20 °C) |
| Melting point | 7.2 °C (45.0 °F; 280.3 K) |
| Boiling point | 232.5 °C (450.5 °F; 505.6 K) |
| Miscible | |
| Solubility | Reacts with haloacids Misicble with acetone, benzene, chloroform, diethyl ether, ethanol, methanol, THF, toluene |
| Vapor pressure | 0.03 mmHg at 20 °C |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich |
| Flash point | 104.4 °C (219.9 °F; 377.5 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Hexamethylphosphoramide, often abbreviated HMPA, is a phosphoramide (an amide of phosphoric acid) with the chemical formula [(CH3)2N]3PO. This colorless liquid is a useful polar aprotic solvent and additive in organic synthesis, albeit it's somewhat exotic for the hobby chemist, since it's not often encountered.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
When heated to decomposition, HMPA emits very toxic fume of phosphine, phosphorus oxides and nitrogen oxides.
Compounds containing a nitrogen–phosphorus bond typically are degraded by the action of hydrochloric acid to form a protonated amine and phosphate. As such, this is a convenient neutralization method.
HMPA dissolves alkali metals forming blue solutions of solvated electrons which are stable for a few hours.
Dimethyl sulfoxide can often be used in place of HMPA as a cosolvent. Both are strong hydrogen bond acceptors, and their oxygen atoms bind metal cations.
Physical
HMPA is a colorless liquid, miscible with water. Old samples appear more yellow or amber.
Availability
HMPA is sold by chemical suppliers though it's not very cheap
Preparation
HMPA can be prepared by reacting phosphoryl chloride and dimethylamine in a liquid diluent.[2]
Projects
- Solvent and high temperature solvent
- Make molybdenum peroxide complexes
Handling
Safety
HMPA is only mildly toxic but has been shown to cause nasal cancers in rats. HMPA can be degraded to less toxic compounds by the action of hydrochloric acid.
Storage
In closed bottles, in a cabinet.
Disposal
Can be degraded by the action of hydrochloric acid.
References
- ↑ Vorob'ev, A. F.; Yakovlev, P. N.; Russian Journal of Physical Chemistry; vol. 56; nb. 8; (1982); p. 1181 - 1183; Zhurnal Fizicheskoi Khimii; vol. 56; nb. 8; (1982); p. 1933 - 1936
- ↑ https://patents.google.com/patent/US3991110A/en