Difference between revisions of "Potassium antimony tartrate"
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
| BoilingPtC = | | BoilingPtC = | ||
| BoilingPt_ref = | | BoilingPt_ref = | ||
| − | | BoilingPt_notes = | + | | BoilingPt_notes = Decomposes |
| Density = 2.6 g/cm<sup>3</sup> | | Density = 2.6 g/cm<sup>3</sup> | ||
| Formula = K<sub>2</sub>Sb<sub>2</sub>(C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>6</sub>)<sub>2</sub> • 3 H<sub>2</sub>O | | Formula = K<sub>2</sub>Sb<sub>2</sub>(C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>6</sub>)<sub>2</sub> • 3 H<sub>2</sub>O | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
| MeltingPtC = | | MeltingPtC = | ||
| MeltingPt_ref = | | MeltingPt_ref = | ||
| − | | MeltingPt_notes = | + | | MeltingPt_notes = Decomposes |
| Odor = Odorless | | Odor = Odorless | ||
| pKa = | | pKa = | ||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
| Solubility1 = 6.6 g/100 ml | | Solubility1 = 6.6 g/100 ml | ||
| Solvent1 = glycerol | | Solvent1 = glycerol | ||
| − | | VaporPressure = | + | | VaporPressure = ~0 mmHg |
}} | }} | ||
| Section3 = {{Chembox Structure | | Section3 = {{Chembox Structure | ||
| Line 91: | Line 91: | ||
| AutoignitionPt = | | AutoignitionPt = | ||
| ExploLimits = | | ExploLimits = | ||
| − | | ExternalMSDS = | + | | ExternalMSDS = [https://www.docdroid.net/i0rN2J4/potassium-antimony-tartrate-trihydrate-sa.pdf.html Sigma-Aldrich] |
| FlashPt = | | FlashPt = | ||
| LD50 = 110 mg/kg | | LD50 = 110 mg/kg | ||
| Line 109: | Line 109: | ||
}} | }} | ||
}} | }} | ||
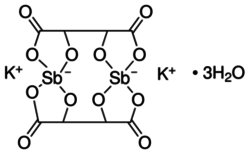
| − | '''Potassium antimony tartrate''' is a [[double salt]] containing potassium and antimony(III) cations and [[tartrate]] anions. It has the formula K<sub>2</sub>Sb<sub>2</sub>(C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>6</sub>)<sub>2</sub> • 3 H<sub>2</sub>O | + | '''Potassium antimony tartrate''' is a [[double salt]] containing potassium and antimony(III) cations and [[tartrate]] anions. It has the formula '''K<sub>2</sub>Sb<sub>2</sub>(C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>6</sub>)<sub>2</sub> • 3 H<sub>2</sub>O''' |
==Properties== | ==Properties== | ||
Revision as of 20:20, 29 June 2017

| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Potassium antimony tartrate
| |
| Other names
Antimony potassium tartrate
Potassium antimonyl tartrate Tartar emetic | |
| Properties | |
| K2Sb2(C4H2O6)2 • 3 H2O | |
| Molar mass | 667.87 g/mol |
| Appearance | White, triangular crystals |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 2.6 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | Decomposes |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
| 8.3 g/100 ml at 0 ºC 33.3 g/100 ml at 100 ºC | |
| Solubility | Insoluble in ethanol, toluene |
| Solubility in glycerol | 6.6 g/100 ml |
| Vapor pressure | ~0 mmHg |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (Median dose)
|
110 mg/kg |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds
|
Tartaric acid |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Potassium antimony tartrate is a double salt containing potassium and antimony(III) cations and tartrate anions. It has the formula K2Sb2(C4H2O6)2 • 3 H2O
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Physical
Potassium antimony tartrate is a white, crystalline compound that crystallizes as flat, triangular crystals.
Availability
Potassium antimony tartrate is used sometimes by biologists studying animal diets to induce vomiting in captured animals. It is available in some developing countries as a quack treatment for alcoholism and other maladies.
Preparation
Potassium antimony tartrate is easily prepared by heating a slurry containing a stoichiometric ratio of potassium bitartrate and antimony trioxide in water to reflux for 15 to 30 minutes. At this time, most if not all of the solid should have dissolved, leaving a colorless solution. The solution is then filtered to remove any remaining reactants, and cooled in the fridge or freezer. As the solution cools, white, triangular crystals of potassium antimony tartrate form. See the relevant thread for a more detailed description.
Wikipedia claims that this compound can also be made from tartaric acid and antimony trioxide, but this is clearly false, as there would be no potassium ions present.
Projects
- Medical drug
Handling
Safety
Potassium antimony tartrate is toxic due to its antimony content, and will induce persistent vomiting if ingested.
Storage
This compound must be stored away from children and pets due to its toxicity. It may be stored with general reagents in the lab.
Disposal
Antimony compounds are toxic to the environment, and should be disposed of as hazardous waste.
References
- X-ray crystallography study of potassium antimony tartrate
- CRC Handbook, 66th Edition (solubility info)
- Wikipedia