Difference between revisions of "Lead styphnate"
| Line 127: | Line 127: | ||
==Preparation== | ==Preparation== | ||
| − | Lead styphnate can be made by reacting [[styphnic acid]] with lead(II) hydroxide or carbonate. Another route involves reacting magnesium styphnate with [[lead(II) acetate]] in water, and , since lead styphnate is practically insoluble in water, it will precipitate out of the solution. Filter the precipitate and wash it with water. | + | Lead styphnate can be made by reacting [[styphnic acid]] with lead(II) hydroxide or carbonate. Another route involves reacting magnesium styphnate with [[lead(II) acetate]] in water, and, since lead styphnate is practically insoluble in water, it will precipitate out of the solution. Filter the precipitate and wash it with water. |
| − | Styphnic acid can be prepared from the nitration of [[resorcinol]] with a mixture of [[nitric|nitric | + | Styphnic acid can be prepared from the nitration of [[resorcinol]] with a mixture of [[nitric acid|nitric]] and [[sulfuric acid]], known as [[nitrating mixture]]. This reaction must be done at low and constant temperature, to prevent a runaway or worse. |
==Projects== | ==Projects== | ||
Latest revision as of 17:17, 13 May 2020
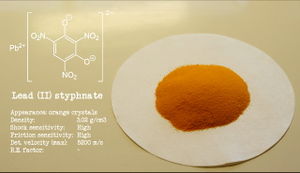 Lead styphnate powder
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Lead(II) 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene-1,3-bis(olate)
| |
| Preferred IUPAC name
Lead(II) 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene-1,3-bis(olate) | |
| Other names
Lead 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene-1,3-diolate
Lead 2,4,6-trinitro-m-phenylene dioxide 1,3-Benzenediol, 2,4,6-trinitro-, lead(2+) salt (1:1) Lead tricinate Lead trinitroresorcinate Tricinat | |
| Properties | |
| C6HN3O8Pb | |
| Molar mass | 450.288 g/mol |
| Appearance | Reddish-orange solid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 3.06 g/cm3 (20 °C) |
| Melting point | 330 °C (626 °F; 603 K) (detonates) |
| Boiling point | Detonates |
| Insoluble | |
| Solubility | Insoluble in most organic solvents. |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | CPCB |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds
|
Styphnic acid |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Lead styphnate is the lead salt of styphnic acid. It is a primary explosive used in detonators.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Lead styphnate detonates when exposed to heat, friction and shock. Its decomposition gives off carbon dioxide, monoxide, water vapor, lead oxide and soot particles.
Physical
Lead styphnate is a reddish-orange solid, almost insoluble in water and most solvents.
Explosive
Lead styphnate is very sensitive to shock and heat. It has a detonation velocity of 5200 m/s.
Availability
Lead styphnate can be found in some detonators, but it's not worth the effort to extract it.
Manufacturing, storing and handling this compound may require an explosive permit.
Preparation
Lead styphnate can be made by reacting styphnic acid with lead(II) hydroxide or carbonate. Another route involves reacting magnesium styphnate with lead(II) acetate in water, and, since lead styphnate is practically insoluble in water, it will precipitate out of the solution. Filter the precipitate and wash it with water.
Styphnic acid can be prepared from the nitration of resorcinol with a mixture of nitric and sulfuric acid, known as nitrating mixture. This reaction must be done at low and constant temperature, to prevent a runaway or worse.
Projects
- Primary explosive in detonators.
Handling
Safety
Lead styphnate is extremely toxic. It is also a sensitive explosive.
Storage
Lead styphnate should be stored in anti-static closed containers. Do not store it for too long.
Disposal
Controlled oxidation, using an oxidizing mixture such as chromic acid, piranha solution or Fenton's reagent will reduce lead styphnate to carbon oxide, water, nitrogen and lead(II) sulfate/chromate. The resulting insoluble lead compounds can either be recycled or taken to hazardous waste disposal centers.
This method however, is not something any amateur can do safely!