Methyl formate
 Freshly distilled methyl formate, made from 85% formic acid and methanol.
| |
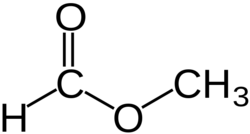 Chemical structure
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Methyl formate
| |
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methyl formate | |
| Other names
R-611
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 60.05 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless volatile liquid |
| Odor | Fruity, lemonade-like |
| Density | 0.987 g/cm3 (15 °C) 0.98 g/cm3 (20 °C) |
| Melting point | −100 °C (−148 °F; 173 K) |
| Boiling point | 31–32 °C (88–90 °F; 304–305 K) |
| 30 g/100 ml (20 °C) 23 g/100 ml (25 °C) | |
| Solubility | Miscible with glacial acetic acid, acetone, chloroform, ethanol, methanol |
| Vapor pressure | 476 mmHg (20 °C) |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Simga-Aldrich |
| Flash point | −19 °C |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (Median dose)
|
1,500 mg/kg (rat, oral) 1,622 mg/kg (rabbit, oral) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds
|
Ethyl formate Methyl acetate |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Methyl formate or methyl methanoate, is the methyl ester of formic acid, the simplest ester.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Methyl formate can be hydrolyzed to methanol and formic acid using a strong acid.
Aminolysis of methyl formate gives formamide or dimethylformamide.
Like its precursor, methanol, methyl formate burns with a nearly invisible flame.
Physical
Methyl formate is a colorless organic liquid, with an ethereal odor, low surface tension and high vapor pressure. It has a melting point of −100 °C and boils at 32 °C. Methyl formate has a density of 0.97 g/cm3 at standard conditions. It is soluble in water (30 g/100 ml) and other solvents, such as acetone, diethyl ether, ethanol, ethyl acetate. The flash point of methyl formate is -19 °C and its auto-ignition temperature is 449 °C.
Availability
Methyl formate is available from chemical suppliers.
Preparation
Methyl formate can be synthesized by reacting anhydrous formic acid with dry methanol, over a strong desiccant, such as calcium chloride. The addition of calcium chloride isn't necessary, but it helps to limit the amount of water being pushed in the condenser by the boiling methyl formate vapors and can also act as boiling chips, which is very important, as due to its low boiling point, methyl formate may bump if the heating element heats the flask too much, unless you have very good temperature control. The resulting distillate is purified by salting out the water and methanol impurities with anh. calcium chloride, followed by drying with anhydrous MgSO4. Due to its low boiling point, methyl formate can be easily purified via fractional distillation.
Industrially, it is prepared by via carbonylation of methanol, using sodium methoxide as a catalyst and pyridine as a temperature promoter, in an extremely dry medium. The smallest traces of water can disrupt the reaction.
- CH3OH + CO → HCOOCH3[1]
This route however is uneconomical for the amateur chemist, thus the first method is cheaper and more accessible.
Projects
- Formamide synthesis
- Organic extractions
Handling
Safety
Methyl formate vapors may irritate lungs, so it's best to work in a well ventilated area. Since its boiling point is lower than the human body temperature, samples of methyl formate should not be kept too long in hand.
Storage
Due to its low boiling point, methyl formate should be stored in closed bottles, away from any source of heat or light, preferable in a fridge. This is mandatory during hot summers.
Disposal
Methyl formate can be safely burned.