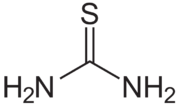
Thiourea
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Thiourea
| |
| Preferred IUPAC name
Thiourea | |
| Other names
Thiocarbamide
| |
| Properties | |
| CH4N2S SC(NH2)2 | |
| Molar mass | 76.12 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.405 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 182 °C (360 °F; 455 K) |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
| 13.7 g/100 ml (25 °C) 14.2 g/100 ml (25 °C) | |
| Solubility | Reacts with acids Soluble in ethanol, methanol Almost insoluble in diethyl ether, hexane |
| Solubility in ethanol | 3.6 g/100 ml (20 °C) 4.7 g/100 ml (31.9 °C) 6.3 g/100 ml (45 °C) 8.5 g/100 ml (58 °C) 9.8 g/100 ml (64.7 °C) |
| Solubility in methanol | 11.9 g/100 ml (25 °C) 16.4 g/100 ml (40.7 °C) 22 g/100 ml (53.7 °C) 24.6g/100 ml (61.9 °C) |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (Median dose)
|
1,750 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds
|
Urea N-Allylthiourea |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Thiourea is an organosulfur compound with the formula SC(NH2)2. It is structurally similar to urea, except that the oxygen atom is replaced by a sulfur atom, thus the properties of urea and thiourea differ significantly.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
Oxidation of thiourea with hydrogen peroxide produces thiourea dioxide
Physical
Thiourea is a colorless white solid, soluble in water. It is odorless and has a taste, often described as bitter. It sublimes under vacuum between 150-160 °C.
Availability
Thiourea is sold by many lab and chemical suppliers.
The liquid silver cleaning product TarnX contains thiourea, a detergent and sulfamic acid.
Preparation
Thiourea can be easily produced from ammonium thiocyanate via heat treatment at 180 °C.
Industrially it is produced by the reaction of hydrogen sulfide with calcium cyanamide in the presence of carbon dioxide.
Projects
- Make thiourea peroxide
- Silver polishing
- Preparation of pharmaceuticals
- Auxiliary agent in diazo paper
- Reducing peroxides to the corresponding diols
- Converting alkyl halides to thiols
Handling
Safety
Thiourea displays average toxicity. The LD50 values given in literature are between 125 and 1,750 mg/kg for rats (oral dose).
A goitrogenic effect (enlargement of the thyroid gland) has been reported for chronic exposure, reflecting the ability of thiourea to interfere with iodide uptake.[1]
Storage
In closed plastic bottles.
Disposal
Thiourea can be neutralized with a strong oxidizing solution.