Difference between revisions of "Ricinoleic acid"
(→Handling) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 126: | Line 126: | ||
==Projects== | ==Projects== | ||
| + | *Synthesis of [[phenylacetylrinvanil]] (a synthetic analogue of [[capsaicin]], but 300 times more potent) | ||
*Make deodorant | *Make deodorant | ||
*Make sodium ricinoleate | *Make sodium ricinoleate | ||
| Line 133: | Line 134: | ||
==Handling== | ==Handling== | ||
===Safety=== | ===Safety=== | ||
| − | Ricinoleic acid has low toxicity, though like it's parent oil it's a powerful laxative if ingested. | + | Ricinoleic acid has low toxicity, though, like it's parent oil, it's a powerful laxative if ingested. |
| − | Since ricin, the toxic protein from the castor beans, is insoluble in castor oil and most organic solvents, there is no risk of poisoning, if you're exposed to crude castor oil or ricinoleic acid. | + | Since ricin, the toxic protein from the castor beans, is insoluble in castor oil and most organic solvents, there is no risk of poisoning, if you're exposed to crude castor oil or ricinoleic acid. However, impure castor oil may contain traces of ricinine, which is harmful. |
===Storage=== | ===Storage=== | ||
| − | Ricinoleic acid is | + | Ricinoleic acid is not stable for long periods of time, and will slowly polymerize when kept in storage. As such, it should be kept in the form of castor oil triglyceride, and prepared just before use. |
===Disposal=== | ===Disposal=== | ||
Latest revision as of 09:16, 25 June 2023
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(9Z,12R)-12-Hydroxyoctadec-9-enoic acid
| |
| Other names
(R)-12-Hydroxy-9-cis-octadecenoic acid
12-Hydroxy-9-cis-octadecenoic acid Ricinelaidic acid Ricinic acid | |
| Properties | |
| C18H34O3 | |
| Molar mass | 298.461 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless oily liquid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 0.945 g/cm3 (20 °C)[1] |
| Melting point | 5.5 °C (41.9 °F; 278.6 K) [3] |
| Boiling point | 242 °C (468 °F; 515 K) [2] |
| 0.346 g/100 ml (at 25 °C) | |
| Solubility | Miscible with benzene, chloroform, diethyl ether |
| Vapor pressure | 4.49·10-3 mmHg at 25 °C |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich |
| Flash point | 224 °C (435.2 °F; 497 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
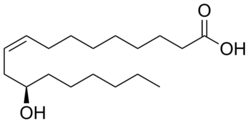
Ricinoleic acid, is an unsaturated omega-9 hydroxy fatty acid. It is a major component of the seed oil obtained from mature castor plant seeds (Ricinus communis L., Euphorbiaceae). About 90% of the fatty acid content in castor oil is the triglyceride formed from ricinoleic acid. The compound is chiral, and occurs naturally as the dextro isomer.
Contents
Properties
Chemical
The compounds can be hydrolyzed to various long chain alcohols.
Physical
Ricinoleic acid is a colorless viscous liquid, immiscible with water but miscible with many organic solvents.
Availability
Ricinoleic acid is sold by chemical suppliers.
Can be easily obtained via saponification of castor oil.
Preparation
Ricinoleic acid can be easily made by saponification of castor oil. For better purification, fractional distillation can be employed. Due to its high boiling point, vacuum distillation is often employed.
Projects
- Synthesis of phenylacetylrinvanil (a synthetic analogue of capsaicin, but 300 times more potent)
- Make deodorant
- Make sodium ricinoleate
- Make zinc ricinoleate
- Make methyl ricinoleate
Handling
Safety
Ricinoleic acid has low toxicity, though, like it's parent oil, it's a powerful laxative if ingested.
Since ricin, the toxic protein from the castor beans, is insoluble in castor oil and most organic solvents, there is no risk of poisoning, if you're exposed to crude castor oil or ricinoleic acid. However, impure castor oil may contain traces of ricinine, which is harmful.
Storage
Ricinoleic acid is not stable for long periods of time, and will slowly polymerize when kept in storage. As such, it should be kept in the form of castor oil triglyceride, and prepared just before use.
Disposal
No special disposal is required. Can be burned or poured down the drain.
References
- ↑ Straus; Heinze; Salzmann; Chemische Berichte; vol. 66; (1933); p. 638
- ↑ Narasimhan; Kothawade; Pharande; Mourya; Dhake; Indian Journal of Chemistry - Section B Organic and Medicinal Chemistry; vol. 42; nb. 11; (2003); p. 2828 - 2834
- ↑ Ibrahim, Sarah A.; Li, S. Kevin; Pharmaceutical Research; vol. 27; nb. 1; (2010); p. 115 - 125